Article Detail
Assessment of Marine Pollution and MARPOL Applications in Mersin Province with Legal Recommendations for Sustainable Fisheries Management
Keywords:
MARPOL
sustainable fishing
marine pollution
Mersin Bay
Mediterranean Sea
port state control
Abstract
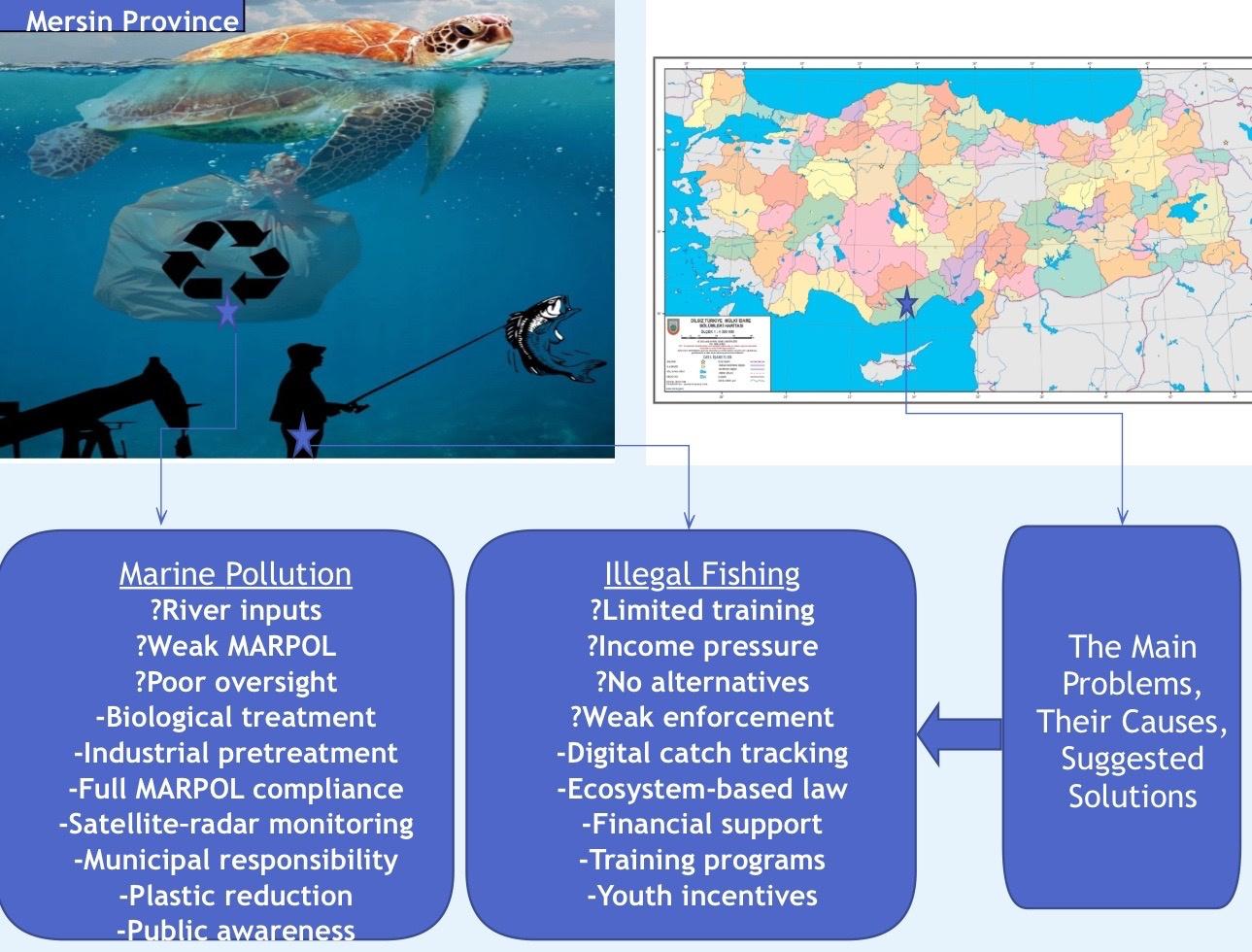
Mediterranean Sea, a semi-enclosed marine system, is increasingly fragile due to rising ship traffic, illegal fishing, microplastic pollution, and land-based contaminants. Mersin, a major port in the Eastern Mediterranean, lies at the intersection of these pressures while hosting trade, tourism, and fishing activities of strategic importance. This study, based on institutional interviews and field analyses conducted in Mersin in 2025, evaluates the local applicability of MARPOL 1973, marine pollution dynamics, and sustainable fishing policies in a multidimensional framework. Findings reveal that pollutants affecting Mersin’s coast are both local and regional, with agricultural drainage, pesticides, heavy metals, and detergent residues transported via the Berdan and Seyhan rivers. These accumulate in coastal ecosystems, intensifying stress on biodiversity. The absence of biological treatment units in wastewater plants and limited regulatory oversight in maritime domains further hinder MARPOL’s effective implementation. Microplastics were detected in fish digestive systems and sediments, highlighting risks of toxic bioaccumulation for ecosystems and public health. In fisheries, despite digital monitoring through the BAGIS system, economic pressures, insufficient education, and unlicensed practices perpetuate illegal fishing. Weak institutional support for small-scale fishers undermines sustainability objectives. The study recommends Türkiye’s stronger engagement in regional governance mechanisms (REMPEC, UNEP/MAP) and acceleration of SECA preparations. The case of Mersin illustrates that sustainable marine management requires not only technical and legal measures but also integrated regional cooperation, infrastructure investment, and local awareness initiatives to safeguard biodiversity and community livelihoods.
References
- Akarsu, C., Kumbur, H., Gökdağ, K., Kıdeyş, A.E., Sanchez-Vidal, A. (2020). Microplastics composition and load from three wastewater treatment plants discharging into Mersin Bay, north eastern Mediterranean Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 150, 110776.
- Aydın, C., Güven, O., Salihoğlu, B., Kideys, A.E. (2016). The Influence of land use on coastal litter: An approach to identify abundance and sources in the coastal area of Cilician Basin, Turkey. Turkish Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 16, 29-39.
- Bayar, S. (2024). Evaluation of port state control inspections in Türkiye. Marine Science and Technology Bulletin, 13(1), 81-93.
- Benzer, R., Benzer, S. (2018). Forecasting the nitrate pollution of groundwater and surface waters: Kütahya example. Karaelmas Science and Engineering Journal, 8(1), 279-287.
- Boran, L.J. (2017). Natural and human induced nutrient impacts on phytoplankton communities in Mersin Bay, NE Mediterranean. Middle East Technical University, Institute of Marine Sciences. Mersin, p 302.
- Bulut, M. Birben, Ü. (2019). Effect of the EU Water Framework Directive on water resources management in Turkey. Turkish Journal of Forestry, 20(3), 221-233.
- Carpenter, A., Donner, P., Johansson, T. (2017). The Role of REMPEC in Marine Pollution Preparedness and Response in the Mediterranean Sea. In Marine Pollution: Current Status and Future Solutions (pp. 197-215). Springer.
- Çevik, C., Kıdeyş, A.E., Tavşanoğlu, Ü.N., Kankılıç, G.B., Gündoğdu, S. (2022). A review of plastic pollution in aquatic ecosystems of Turkey. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(18), 26230-26249.
- De Nooijer, L.J. (2007). Shallow water benthic foraminifera as proxy for natural versus human-induced environmental change. Utrecht University, Faculty of Geosciences. Utrecht, p 152.
- Demir, İ. (2011). The assesment of “The act on principles of intervention in urgent cases of pollution of the Sea environment by oil and other noxious items and compensation for damage” in terms of civil liability and compensation principles for damage. Journal of İnönü University Faculty of Law, 2(1), 239-324.
- Diaz, R. J., Rosenberg, R. (2008). Spreading dead zones and consequences for marine ecosystems. Science, 321(5891), 926-929.
- Doğan-Sağlamtimur, N., Subaşı, E. (2018). Ship generated marine pollution and waste reception facilities from the World and Turkey: General perspective, management and suggestions. Pamukkale University Journal of Engineering Sciences, 24(3), 481-493.
- FAO. (2022). The state of world fisheries and aquaculture 2022: Towards blue transformation. FAO.
- Galgani, F., Hanke, G., Maes, T. (2019). Global distribution, composition and abundance of marine litter. In Marine Anthropogenic Litter (pp. 29-56). Springer.
- Güven, O., Gökdağ, K., Jovanovic, B., Kıdeyş, A.E. (2017). Microplastic litter composition of the Turkish territorial waters of the Mediterranean Sea, and its occurrence in the gastrointestinal tract of fish. Environmental Pollution, 223, 286-294.
- Kanlı, İ.B., Falcıoğlu, N.N. (2021). The importance of the environmental cooperation in protection of the Mediterranean Sea and its coasts through the Barcelona Convention. IBAD Journal of Social Sciences, 9, 117-142.
- Koçak, M., Kubilay, N., Tuğrul, S., Mihalopoulos, N. (2010). Long-term atmospheric nutrient inputs to the Eastern Mediterranean: sources, solubility and comparison with riverine inputs. Biogeosciences Discuss, 7, 5081-5117.
- Öztürk, B. (2009). Marine protected areas in the high seas of the Aegean and Eastern Mediterranean Seas, some proposals. Journal of Black Sea/Mediterranean Environment, 15(1), 69-82.
- Raftopoulos, E. (2011). The Mediterranean Response to Global Challenges: Environmental Governance and the Barcelona Convention System. In The World Ocean in Globalisation (pp. 507-538). Brill Nijhoff.
- Satır, T. (2007). Developing port reception facility model in the Turkish ports for establish and management sufficent for international convention for the prevention of pollution from ships. Istanbul University, Institute of Marine Sciences and Management. İstanbul, p 137.
- Schroeder, A. (2003). Community dynamics and development of soft bottom macrozoobenthos in the German Bight (North Sea). Bremen University, Faculty 2 Biology/Chemistry. Bremen, p 190.
- Turan, M. (2009). Turkey’s oil spill response policy: Influences and implementation. United Nations.
- Uçar, A. (2025). Prevention of pollution from sewage on passenger ships: a comparison between international and Turkish regulations. How can artificial intelligence (ai) help to improve the most common issues with sewage systems?. Journal of Yeditepe University Faculty of Law, 22(2), 921-956.
- Ünal, V., Ertör, I., Ertör-Akyazi, P., Tunca, S. (2022). Making Pescatourism Just for Small-Scale Fisheries: The Case of Turkey and Lessons for Others. In Blue Justice: Small-Scale Fisheries in a Sustainable Ocean Economy (pp. 315-333). Springer.
- Yılmaz, N.P. (2024). Türkiye’s harmonization with the EU’s Maritime Policies: An analysis in the framework of the EU country reports between 2018 and 2023. International Journal of Social Inquiry, 17(3), 449-466.
40
31643
137054
20days
50days
10days
