Article Detail
Determining the Bioecological Characteristics of Invasive Lionfish Species (Pterois spp.) in the Northeastern Mediterranean
Keywords:
Lionfish
Pterois spp.
invasive species
bioecological characteristics
northeastern Mediterranean
Türkiye
Abstract
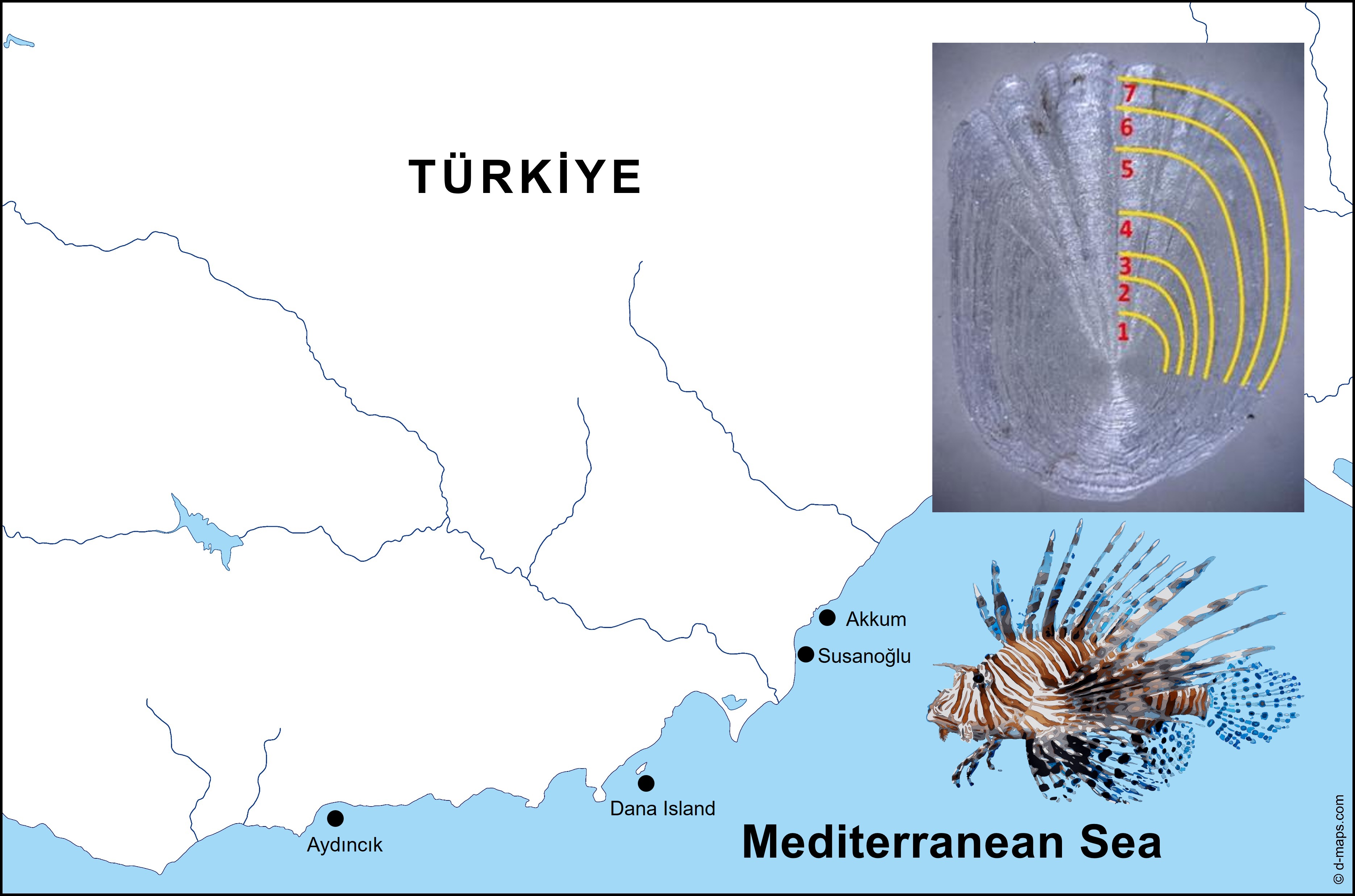
The present study investigated the bioecology of invasive lionfish species (Pterois spp.) through regular dives along the Mersin coastline, northeastern Mediterranean. The length, weight, age, stomach contents and gonads of the collected lionfish were analyzed, and the environmental parameters such as seawater temperature, depth, pH and salinity at the sampling stations were also recorded. The total lengths ranged from 6.0 to 38.0 cm and the weights ranged from 1.3 to 769.0 g. The length-weight relationships were calculated for all individuals as W = 0.049 x L3.30. The growth pattern was detected as positive allometric. The maximum age class was VII for all individuals. The von Bertalanffy growth parameters were L∞ = 45.35 cm, W∞ = 1435 g, k = 0.061 year-1, t0 = -6.282 years. The stomach contents were found to be predominantly composed of small fish, accounting for 77.5% of the total weight, while invertebrates constituted a smaller proportion (5.9%). The mean gonad weight of 191 females was 4.52 g, with a maximum of 60 g. Mean egg diameter measured 1.3 mm, and females averaged 74 eggs. Gonadosomatic index and condition factor analyses show reproduction peaks in summer. Lionfish proliferation in the eastern Mediterranean is driven by venomous spines, rapid growth, early maturation, hunting success, and opportunistic feeding. Findings highlight rapid growth, high fecundity, and dietary overlap with native predators, suggesting sustainable control requires protecting natural predators and targeted removals.
References
- Albins, M.A., Hixon, M.A. (2008). Invasive Indo-Pacific lionfish Pterois volitans reduce recruitment of Atlantic coral-reef fishes. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 367, 233-238.
- Albins, M.A. (2013). Effects of invasive Pacific red lionfish Pterois volitans versus a native predator on Bahamian coral-reef fish communities. Biological Invasions, 15(1), 29-43.
- Alkan, Ö., Ayaz, A., Altınağaç, U., Özekinci, U., Çakır, F., Daban, İ.B., Şen, Y., Uğur G.E., Ayaz O. (2023). An additional record of lionfish Pterois miles (Bennett, 1828) in Edremit Bay. Doğanın Sesi, 6(12), 19-28.
- Andradi-Brown, D.A., Grey, R., Hendrix, A., Hitchner, D., Hunt, C.L., Gress, E., Madej, K., Parry, R.L., Regnier-McKellar, C., Jones, O.P., Arteaga, M., Izaguirre, A.P., Rogers, A. D., Exton, D.A. (2017). Depth-dependent effects of culling—Do mesophotic lionfish populations undermine current management? Royal Society Open Science, 4(5), 170027.
- Arbuatti, A., Lucidi, P. (2010). Reef aquariofily: a hobby for everyone? How an adequate knowledge of Pterois volitans’ behavior and welfare can avoid risks and accidents. Aquaculture, Aquarium, Conservation & Legislation, 3(1), 9-16.
- Avşar, D. (2005). Fisheries biology and population dynamics. Nobel Bookstore Publications.
- Ayas, D., Şen Ağılkaya, G., Yağlıoğlu, D. (2018). New record of the red lionfish, Pterois volitans (Linnaeus, 1758), inthe Northeastern Mediterranean Sea. Düzce University Journal of Science & Technology, 6(4), 871-877.
- Bagenal, T.B., Tesch, F.W. (1978). Age and growth. In Methods for Assessment of Fish Production in Fresh Waters (pp. 101-136). Blackwell Scientific Publications.
- Baker, R., Buckland, A., Sheaves, M. (2014). Fish gut content analysis: robust measures of diet composition. Fish and Fisheries, 15(1), 170-177.
- Barbour, A.B., Allen, M.S., Frazer, T.K., Sherman, K.D. (2011). Evaluating the potential efficacy of invasive lionfish (Pterois volitans) removals. PLoS One, 6(5), e19666.
- Bariche, M., Torres, M., Azzurro, E. (2013). The presence of the invasive lionfish Pterois miles in the Mediterranean Sea. Mediterranean Marine Science, 14(2), 292-294.
- Benkwitt, C.E. (2016). Invasive lionfish increase activity and foraging movements at greater local densities. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 558, 255-266.
- Bilge, G., Filiz, H., Yapıcı, S., Gülşahin, A. (2016). On the occurrence of the devil firefısh Pterois miles (Scorpaenidae), from the southern Aegean Sea with an elaborate occurrences in the Mediterranean coast of Turkey. In: Book of Proceedings. HydroMediT 2016 2nd International Congress on Applied Ichthyology and Aquatic Environment, 10-12 November 2016, Messolonghi, Greece, pp. 324-327.
- Chin, D.A., Aiken, K.A., Buddo, D. (2016). Lionfish population density in Discovery Bay, Jamaica. International Journal of Scientific and Engineering Research, 7(12), 1327-1331.
- Cote, I.M., Green, S.J., Hixon, M.A. (2013). Predatory fish invaders: insights from Indo-Pacific lionfish in the western Atlantic and Caribbean. Biological Conservation, 164, 50-61.
- Çete H.E., Ergene, S. (2018). Türkiye Doğu Akdeniz Bölgesi Lagos Balığı: Büyüme Oranları ve Beslenme Özelliklerinin İncelenmesi. Lap Lambert Academic Publishing. [In Turkish].
- Dağhan, H., Demirhan, S. A. (2020). Some bio-ecological characteristics of the lionfish Pterois miles (Bennett, 1828) distributed in the Gulf of Iskenderun. Marine and Life Sciences, 2(1), 28-40.
- Darling, E.S., Green, S.J., O’Leary, J.K., Cote, I.M. (2011). Indo-Pacific lionfish are larger and more abundant on invaded reefs: a comparison of Kenyan and Bahamian lionfish populations. Biological Invasions, 13, 2045-2051.
- Demirci, B., Demirhan, S. A. (2022). Food composition and dietary overlap of the lionfish species in Iskenderun bay. Natural and Engineering Sciences, 7(3), 228-239.
- Eddy, C., Pitt, J., Morris, J. A., Smith, S., Goodbody-Gringley, G., Bernal, D. (2016). Diet of invasive lionfish (Pterois volitans and P. miles) in Bermuda. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 558, 193-206.
- Edwards, M.A., Frazer, T.K., Jacoby, C.A. (2014). Age and growth of invasive lionfish (Pterois spp.) in the Caribbean Sea, with implications for management. Bulletin of Marine Science, 90(4), 953-966.
- Ehemann, N.R., Perez‐Palafox, X.A., Mora‐Zamacona, P., Burgos‐Vazquez, M.I., Navia, A.F., Mejia‐Falla, P.A., Cruz‐Escalona, V.H. (2017). Size-weight relationships of batoids captured by artisanal fishery in the southern Gulf of California, Mexico. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 33(5), 1051-1054.
- Evripidou, S. (2013). Toxic Lionfish makes its way to Cyprus waters. www.cyprus-mail.com/cyprus/toxicLionfish-makes-its-way-cyprus-waters/20130220, version 02/2013).
- Farrag, M., El-Haweet, A.A., Moustafa, M.A. (2016). Occurrence of puffer fishes (Tetraodontidae) in the eastern Mediterranean, Egyptian coast-filling in the gap. BioInvasions Record, 5(1), 47.
- Fishelson, L. (1975). Ethology and reproduction of pteroid fishes found in the Gulf of Aqaba (Red Sea), especially Dendrochirus brachypterus (Cuvier) (Pteroidae: Teleostei). Pubblicazioni della Stazione Zoologica di Napoli, 39, 635-656.
- Fishelson, L. (1997). Experiments and observations on food consumption, growth and starvation in Dendrochirus brachypterus and Pterois volitans (Pteroinae, Scorpaenidae). Environmental Biology of Fishes, 50(4), 391-403.
- Fogg, A.Q., Brown-Peterson, N.J., Peterson, M.S. (2017). Reproductive life history characteristics of invasive red lionfish (Pterois volitans) in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Bulletin of Marine Science, 93(3), 791-813.
- Fogg, A.Q., Evans, J.T., Peterson, M.S., Brown-Peterson, N.J., Hoffmayer, E.R., Ingram, G.W. (2019). Comparison of age and growth parameters of invasive red lionfish (Pterois volitans) across the northern Gulf of Mexico. Fishery Bulletin, 117(3), 1-15.
- Gardner, P.G., Frazer, T.K., Jacoby, C.A., Yanong, R.P. (2015). Reproductive biology of invasive lionfish (Pterois spp.). Frontiers in Marine Science, 2(7), 1-10.
- Golani, D., Sonin, O. (1992). New records of the Red Sea fishes, Pterois miles (Scorpaenidae) and Pteragogus pelycus (Labridae) from the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Japanese Journal of Ichthyology, 39(2), 167-169.
- Golani, D., Öztürk, B., Başusta, N. (2006). Fishes of the eastern Mediterranean. Turkish Marine Research Foundation (TUDAV).
- Gökoğlu, M., Teker, S., Julian, D. (2017). Westward extension of the lionfish Pterois volitans Linnaeus, 1758 along the Mediterranean coast of Turkey. Natural and Engineering Sciences, 2(2), 67-72.
- Green, S.J., Akins, J.L., Maljkovic, A., Cote, I.M. (2012). Invasive lionfish drive Atlantic coral reef fish declines. PLoS One, 7(3), e32596.
- Gürlek, M., Ergüden, D., Uyan, A., Doğdu, S.A., Yağlıoğlu D., Öztürk B., Turan C. (2016). First record red lionfish Pterois volitans (Linnaeus, 1785) in the Mediterranean Sea. Natural and Engineering Sciences, 1(3), 27-32.
- Harms-Tuohy, C.A., Schizas, N.V., Appeldoorn, R.S. (2016). Use of DNA metabarcoding for stomach content analysis in the invasive lionfish Pterois volitans in Puerto Rico. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 558, 181-191.
- Johnson, E.G., Swenarton, M.K. (2016). Age, growth and population structure of invasive lionfish (Pterois volitans/miles) in northeast Florida using a length-based, age-structured population model. PeerJ, 4, e2730.
- Johnston M.W., Purkis S.J. (2014). Are lionfish set for a Mediterranean invasion? Modelling explains why this is unlikely to occur. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 88, (1-2), 138-147.
- Jud, Z.R., Layman, C.A., Lee, J.A., Arrington, D.A. (2011). Recent invasion of a Florida (USA) estuarine system by lionfish Pterois volitans/P. miles. Aquatic Biology, 13(1), 21-26.
- Jud, Z.R., Layman, C.A. (2012). Site fidelity and movement patterns of invasive lionfish, Pterois spp., in a Florida estuary. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 414, 69-74.
- Kondylatos, G., Theocharis, A., Mandalakis, M., Avgoustinaki, M., Karagyaurova, T., Koulocheri, Z., Vardali, S., Klaoudatos, D. (2024). The devil firefish Pterois miles (Bennett, 1828): life history traits of a potential fishing resource in Rhodes (eastern Mediterranean). Hydrobiology, 3(1), 31-50.
- Kindinger, T.L. (2015). Behavioral response of native Atlantic territorial three spot damselfish (Stegastes planifrons) toward invasive Pacific red lionfish (Pterois volitans). Environmental Biology of Fishes, 98, 487-498.
- Kletou, D., Hall-Spencer, J. M., Kleitou, P. (2016). A lionfish (Pterois miles) invasion has begun in the Mediterranean Sea. Marine Biodiversity Records, 9(1), 46.
- Lagler, K.F. (1956). The pike, Esox lucius Linnaeus, in relation to water-fowl on the Seney National Wildlife Refuge, Michigan. The Journal of Wildlife Management, 20(2), 114-124.
- Le Cren, E.D. (1951). The length-weight relationship and seasonal cycle in gonad weight and condition in the perch (Perca fluviatilis). The Journal of Animal Ecology, 20(2), 201-219.
- Morris, J.A., Alkins, J., Barse, A., Cerino, D., Freshwater, D., Green, S., Munoz, R., Paris, C., Whitfield, P. (2008). Biology and ecology of the invasive lionfishes, P. volitans and P. miles. In: Book of Proceedings. 61st Gulf and Caribbean Fisheries Institute, 10-14 November 2008, Gosier, Guadeloupe, French West Indies. pp. 409-414.
- Morris, J.A. (2009). The biology and ecology of the invasive Indo-Pacific lionfish. North Carolina State University, Graduate Faculty. North Carolina, p 168.
- Oray, I.K., Sınay, E., Karakulak, F.S., Yıldız, T. (2015). An expected marine alien fish caught at the coast of Northern Cyprus: Pterois miles (Bennett, 1828). Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 31(4), 733-735.
- Oruç, A.Ç., Şensurat-Genç, T., Özgül, A., Lök, A. (2022). The northernmost dispersal record of the lionfish, Pterois miles (Bennett, 1828) for the Aegean Sea. Ege Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 39(1), 84-87.
- Otero, P., Rodriguez, P., Botana, A.M., Alfonso, A., Botana, L.M. (2013). Analysis of natural toxins. In Liquid Chromatography (pp. 411-430). Elsevier.
- Özbek, E.Ö., Mavruk, S., Saygu, I., Öztürk, B. (2017). Lionfish distribution in the eastern mediterranean coast of Turkey. Journal of Black Sea/Mediterranean Environment, 23, 1-16.
- Özgül, A. (2020) Occurrence of lionfish, Pterois miles (Bennett, 1828) in the coast of Aegean Sea (Turkey): The northernmost dispersal record. Ege Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 37(3), 313-317.
- Perera-Chan, L., Aguilar-Perera, A. (2014). Length–weight and length–length relationships of the invasive red lionfish [Pterois volitans (Linnaeus, 1758): Scorpaenidae] in the Parque Nacional Arrecife Alacranes, Southern Gulf of Mexico. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 30(1), 202-203.
- Potts, J.C., Berrane, D., Morris, J.A. (2010). Age and growth of lionfish from the Western North Atlantic. In: Book of Proceedings. 63rd Gulf Caribbean Fisheries Institute, 1-5 November 2010, San Juan, Puerto Rico. pp. 313-314.
- Poursanidis D. (2015). Ecological niche modeling of the invasive lionfish Pterois miles (Bennett, 1828) in the Mediterranean Sea. In: Book of Proceedings. 11th Panhellenic Symposium on Oceanography and Fisheries, 13-17 May 2015, Mytilene, Lesvos Island, Greece. pp. 621-624.
- Pusack, T.J., Benkwitt, C.E., Cure, K. Kindinger, T.L. (2016). Invasive red lionfish grow faster in the Atlantic Ocean than in their native Pacific range. Environmental Biology of Fishes, 99(6-7), 571-579.
- Render, J.H., Thompson, B.A., Allen, R.L. (1995). Reproductive development of striped mullet in Louisiana estuarine waters with notes on the applicability of reproductive assessment methods for isochronal species. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society, 124(1), 26-36.
- Ricker, W.E. (1975). Computation and interpretation of biological statistics of fish populations. The Blackburn Press.
- Sabido-Itza, M. M., Aguilar-Perera, A., Medina-Quej, A. (2016). Length–weight and length–length relations, and relative condition factor of red lionfish, Pterois volitans (Actinopterygii: Scorpaeniformes: Scorpaenidae), from two natural protected areas in the Mexican Caribbean. Acta Ichthyologica et Piscatoria, 46(4), 279-285.
- Savva, I., Chartosia, N., Antoniou, C., Kleitou, P., Georgiou, A., Stern, N., Hadjioannou, L., Jimenez, C., Andreou, V., Spencer, M. H., Kletou, D. (2020). They are here to stay: the biology and ecology of lionfish (Pterois miles) in the Mediterranean Sea. Journal of Fish Biology, 97, 148-162.
- Schneider, K., Erez, J. (2006). The effect of carbonate chemistry on calcification and photosynthesis in the hermatypic coral Acropora eurystoma. Limnology and Oceanography, 51(3), 1284-1293.
- South, J., Dick, J.T., McCard, M., Barrios-O’Neill, D., Anton, A. (2017). Predicting predatory impact of juvenile invasive lionfish (Pterois volitans) on a crustacean prey using functional response analysis: effects of temperature, habitat complexity and light regimes. Environmental Biology of Fishes, 100, 1155-1165.
- Sparre, P., Venema, S. C. (1992). Introduction to tropical fish stock assessment. Part 1: Manual. FAO.
- Stamouli, C., Akel, E. H. K., Azzurro, E., Bakiu, R., Bas, A. A., Bitar, G., Boyacı, Y., Cakalli, M., Corsini-Foka, M., Crocetta, F., Dragičević, B., Dulcic, J., Durucan, F., Zrelli, R. E., Erguden, D., Filiz, H., Giardina, F., Giovos, I., Gönülal, O., Hemida, F., Kassar, A., Kondylatos, G., Macali, A., Mancini, E., Ovalis, P., Paladini De Mendoza, F., Pavicic, M., Rabaoui, L., Rizkalla, S., Tiralongo, F., Turan, C., Vrdoljak, D., Yapıcı, S., Zenetos, A. (2018). New Mediterranean Biodiversity Records (December 2017). Mediterranean Marine Science, 18(3), 534-556.
- Toledo-Hernandez, C., Velez-Zuazo, X., Ruiz-Diaz, C.P., Patricio, A.R., Mege, P., Navarro, M., Sabat, A.M., Betancur-R.R., Papa, R. (2014). Population ecology and genetics of the invasive lionfish in Puerto Rico. Aquatic Invasions, 9(2), 227-237.
- Turan C., Ergüden D., Gürlek M., Yağlıoğlu D., Uyan A., Uygur N. (2014). First record of the Indo-Pacific lionfish Pterois miles (Bennett, 1828) (Osteichthyes: Scorpaenidae) for the Turkish marine waters. Journal of the Black Sea/Mediterranean Environment, 20(2), 158-163.
- Turan, C., Öztürk, B. (2015). First record of the lionfish Pterois miles (Bennett 1828) from the Aegean Sea. Journal of the Black Sea/Mediterranean Environment, 20(2), 334-388.
- Turan, C., Ergüden, D., Gürlek, M. (2016). Climate change and biodiversity effects in Turkish seas. Natural and Engineering Sciences, 1(2), 15-24.
- Turan, C., Gürlek, M., Başusta, N., Uyan, A., Doğdu, S.A., Karan, S. (2018). A checklist of the non-indigenous fishes in Turkish marine waters. Natural and Engineering Sciences, 3(3), 333-358.
- Turan, C. (2020). Species distribution modelling of invasive alien species; Pterois miles for current distribution and future suitable habitats. Global Journal of Environmental Science and Management, 6(4), 429-440.
- Turan, C., Ergüden, D., Gürlek, M., Doğdu, S.A. (2024) Checklist of alien fish species in the Turkish marine ichthyofauna for science and policy support. Tethys Environmental Science, 1(2), 50-86.
- Ulman, A., Tunçer, S., Kızılkaya, İ.T., Zilifli, A., Alford, P., Giovos, I. (2020). The lionfish expansion in the Aegean Sea in Turkey: a looming potential ecological disaster. Regional Studies in Marine Science, 36, 101271.
- Valdez-Moreno, M., Quintal-Lizama, C., Gomez-Lozano, R., Garcia-Rivas, M.D.C. (2012). Monitoring an alien invasion: DNA barcoding and the identification of lionfish and their prey on coral reefs of the Mexican Caribbean. PLoS One, 7(6), e36636.
- von Bertalanffy, L. (1957). Quantitative laws in metabolism and growth. The Quarterly Review of Biology, 32(3), 217-231.
- Yağlıoğlu D., Ayas D. (2016). New occurrence data of four alien fishes (Pisodonophis semicinctus, Pterois miles, Scarus ghobban and Parupeneus forsskali) from the north eastern Mediterranean (Yeşilovacık Bay, Turkey). Biharean Biologist, 10(2), 150-152.
- Yılmaz, S., Demirhan, S. A. (2020). Age, growth parameters and food composition of Invasive Red Lionfish (Pterois volitans L., 1758) in İskenderun Bay. Natural and Engineering Sciences, 5(2), 82-91.
- Zannaki, K., Corsini-Foka, M., Kampouris, T. E., Batjakas, I. E. (2019). First results on the diet of the invasive Pterois miles in the Hellenic waters. Acta Ichthyologica et Piscatoria, 49(3), 31-40.
- Zenetos, Α., Gofas, S., Morri, C., Rosso, A., Violanti, D., Raso, J.G., Çınar, M.E., Almogi-Labin, A., Ateş, A.S., Azzurro, E., Ballesteros, E., Bianchi, C.N., Bilecenoğlu, M., Gambi, M.C., Giangrande, A., Gravili, C., Hyams-Kaphzan, O., Karachle, P.K., Katsanevakis, S., Lipej, L., Mastrototaro, F., Mineur, F., Pancucci-Papadopoulou, M.A., Ramos Esplá, A., Salas, C., San Martín, G., Sfriso, A., Streftaris, N., Verlaque, M. (2012) Alien species in the Mediterranean Sea by 2012. A contribution to the application of European Union’s Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD). Part 2. Introduction trends and pathways. Mediterranean Marine Science, 13(2), 328-352.
40
31644
137055
20days
50days
10days
