Article Detail
Spatiotemporal Variations in Macrozoobenthic Communities at the Mouth of the Mezitli Stream, Mersin Bay (Northeastern Mediterranean)
Keywords:
Macrozoobenthos
Shannon-Weaver index
Margalef’s richness index
AZTI’s marine biotic index
Mezitli Stream
Türkiye
Abstract
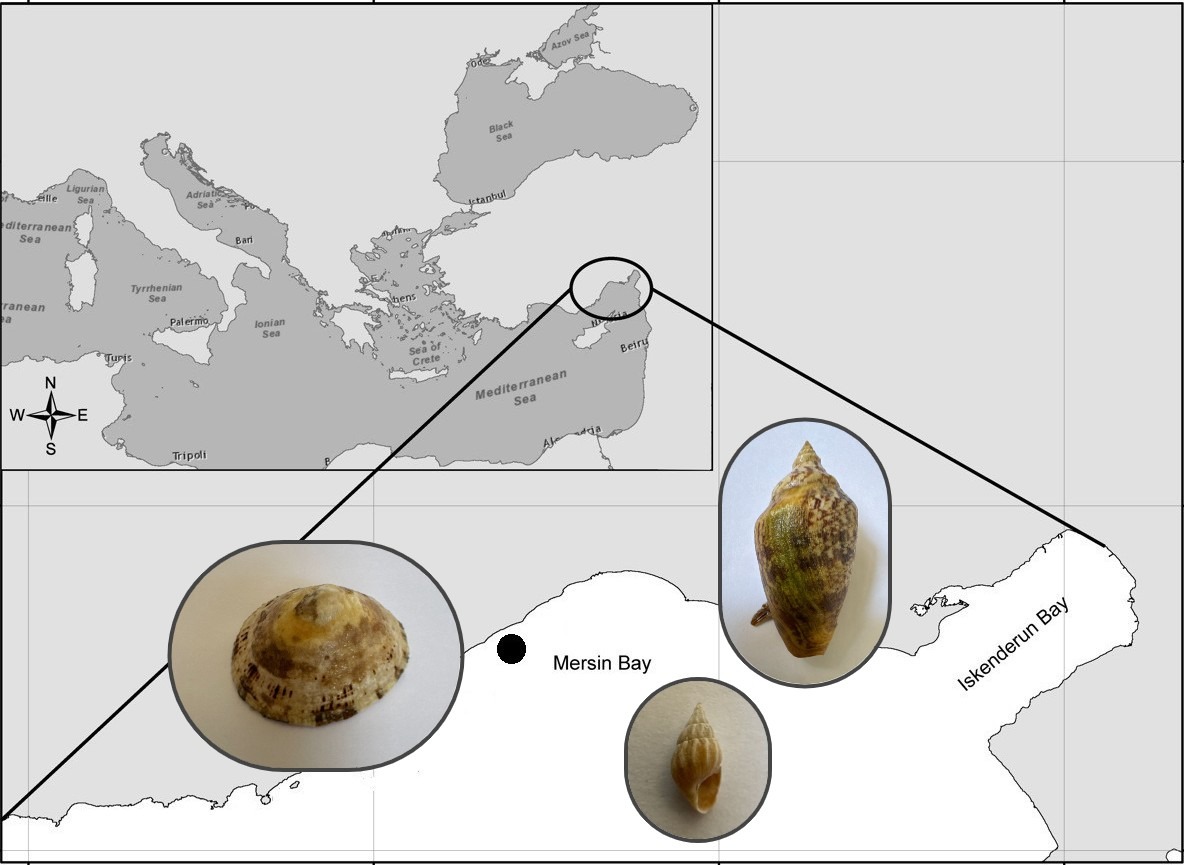
This study evaluated the ecological status of macrozoobenthic communities at the mouth of Mezitli Stream, Mersin Bay, under spatiotemporal variability and pollution pressures. Sediment samples were collected from six stations during dry and wet seasons; Shannon-Weaver Diversity Index, Margalef’s Species Richness Index, and AZTI’s Marine Biotic Index (AMBI) were used to assess ecosystem health. In addition, the oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) of the sediment was measured as a supportive indicator of environmental conditions. During the dry season, low Shannon and Margalef values, together with low ORP levels, were observed, especially at Stations 5 and 6, due to possible oxygen deficiency and degraded benthic structure. These stream-influenced stations stood out as the most degraded areas with high AMBI scores, dominance of tolerant species (Nereis sp., Corbula gibba), and low dissolved oxygen levels. During the wet season, increased freshwater inflow and improved oxygen resulted in richer and more balanced communities (e.g. Alvania discors, Tellina sp. and Mangelia sp.). Despite these conditions, Stations 5 and 6 exhibited lower Shannon, Margalef, AMBI scores and ORP levels. The findings reveal that seasonal changes in organic load and oxygen levels are the main factors determining the structure of the benthic ecosystem in the Mezitli Stream mouth area.
References
- Albayrak, S., Balkis, H., Zenetos, A., Kurun, A., Kubanç, C. (2006). Ecological quality status of coastal benthic ecosystems in the Sea of Marmara. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 52(7), 790-799.
- Allan, D., Erickson, D., Fay, J. (1997). The influence of catchment land use on stream integrity across multiple spatial scales. Freshwater Biology, 37(1), 149-161.
- Attrill, M. J. (2002). A testable linear model for diversity trends in estuaries. Journal of Animal Ecology, 71(2), 262-269.
- Balsamo, M., Semprucci, F., Frontalini, F., Coccioni, R. (2012). Meiofauna as a tool for marine ecosystem biomonitoring. Marine Ecosystems, 4, 77-104.
- Borja, A., Franco, J., Pérez, V. (2000). A marine biotic index to establish the ecological quality of soft-bottom benthos within European estuarine and coastal environments. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 40(12), 1100-1114.
- Borja, A., Chust, G., Muxika, I. (2019). Forever young: the successful story of a marine biotic index. Advances in Marine Biology, 82, 93-127.
- Borja, A., Muxika, I. (2005). Guidelines for the use of AMBI (AZTI’s Marine Biotic Index) in the assessment of the benthic ecological quality. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50(7), 787-789.
- Day, J. W., Hall, C. A. S., Kemp, W. M., Yáñez-Arancibia, A. (1989). Estuarine ecology. John Wiley & Sons.
- de Almeida, T. C. M., Arana, P. M., Sant’Ana, R., Pezzuto, P. R. (2016). A new benthic macrofauna and sediments sampler for attaching to otter trawl nets: comparison with the Van Veen grab. Latin American Journal of Aquatic Research, 44(5), 1116-1122.
- Doğan, A., Önen, M., Ergen, Z., Katağan, T., Çınar, M. E. (2004). Ecological quality assessment in Izmir Bay using the Bentix index. In: Book of Proceedings. Workshop on Marine Sciences & Biological Resources, University of Tishreen, 25-26 May 2004, Lattakia Syria, pp. 25-26.
- Douterelo, I., Perona, E., Mateo, P. (2004). Use of cyanobacteria to assess water quality in running waters. Environmental Pollution, 127(3), 377-384.
- Duarte, C. M. (2009). Coastal eutrophication research: a new awareness. Hydrobiologia, 629(1), 263-269.
- Dudgeon, D., Arthington, A. H., Gessner, M. O., Kawabata, Z.-I., Knowler, D. J., Lévêque, C., Naiman, R. J., Prieur-Richard, A. H., Soto, D., Stiassny, M. L. J., Sullivan, C. A. (2006). Freshwater biodiversity: importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biological Reviews, 81(2), 163-182.
- Eken, M., Akman, B. (2018). Assessment of heavy metal pollution of seston from freshwater resources poured into the Northeast Mediterranean region. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190, 1-7.
- Fenchel, T. M., Riedl, R. J. (1970). The sulfide system: a new biotic community underneath the oxidized layer of marine sand bottoms. Marine Biology, 7(3), 255-268.
- Ge, J., Chen, J., Zi, F., Song, T., Hu, L., He, Z., Wu, L., Ding, Y., Li, H. (2025). Seasonal variations in macrobenthos communities and their relationship with environmental factors in the Alpine Yuqu River. Biology, 14(2), 120.
- Grall, J., Chauvaud, L. (2002). Marine eutrophication and benthos: the need for new approaches and concepts. Global Change Biology, 8(9), 813-830.
- Gray, J. S., Wu, R. S. S., Or, Y. Y. (2002). Effects of hypoxia and organic enrichment on the coastal marine environment. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 238, 249-279.
- Hyland, J., Balthis, L., Karakassis, I., Magni, P., Petrov, A., Shine, J., Vestergaard, O., Warwick, R. (2005). Organic carbon content of sediments as an indicator of stress in the marine benthos. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 295, 91-103.
- İlhan, E. B. B., İnnal, D., Çavuş-Arslan, H., Balkıs, N. Ç. (2024). Risk assessment and pollution loads of potentially toxic elements in water of four rivers flowing into the Mediterranean Sea. Regional Studies in Marine Science, 73, 103451.
- Kazancı, N., Girgin, S., Dügel, M., Oğuzkurt, D. (1997). Akarsuların çevre kalitesi yönünden değerlendirilmesinde ve izlenmesinde biyotik indeks yöntemi. Form Ofset. [In Turkish].
- Kennish, M. J. (2002). Environmental threats and environmental future of estuaries. Environmental Conservation, 29(1), 78-107.
- Koyuncu, C. E., Ayas, D. (2024). Sand steenbras Lithognathus mormyrus (Linnaeus, 1758), the new host of the parasitic isopod Anilocra physodes (Linnaeus, 1758) from Mersin Bay, northeastern Mediterranean. Tethys Environmental Sciences, 1(4), 193-199.
- Kristensen, E. (2000). Organic matter diagenesis at the oxic/anoxic interface in coastal marine sediments, with emphasis on the role of burrowing animals. Hydrobiologia 426, 1-24.
- Margalef, R. (1958). Information theory in biology. General Systems, 3, 36-71.
- Pearson, T. A. (1978). Macrobenthic succession in relation to organic enrichment and pollution of the marine environment. Oceanography and Marine Biology: An Annual Review, 16, 229-311.
- Poff, N. L., Allan, J. D., Bain, M. B., Karr, J. R., Prestegaard, K. L., Richter, B. D., Sparks, R. E., Stromberg, J. C. (1997). The natural flow regime. BioScience, 47(11), 769-784.
- Rosenberg, D. M., Resh, V. (1992). Freshwater biomonitoring using individual organisms, populations, and species assemblages of benthic macroinvertebrates. In Freshwater Biomonitoring and Benthics Macroinvertebrates (pp. 40-158). Chapman & Hall.
- Shannon, C. E., Weaver, W. (1949). The mathematical theory of communication. University of Illinois Press.
- Shirahata, S., Hamasaki, T., Teruya, K. (2012). Advanced research on the health benefit of reduced water. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 23(2), 124-131.
- Turan, C., Ergüden, D., Gürlek, M., Doğdu, S. A. (2024). Checklist of Alien Fish Species in the Turkish Marine Ichthyofauna for Science and Policy Support. Tethys Environmental Science, 1(2), 50-86.
- Turan, C., Uyan, A., Soldo, A., Doğdu, S. A., Ergüden, D. (2025). Checklist of cartilaginous species with current status and conservation strategies in Turkish marine waters. Tethys Environmental Science. 2(1), 31-61.
- Vinson, M. R., Hawkins, C. P. (1998). Biodiversity of stream insects: variation at local, basin, and regional scales. Annual Review of Entomology, 43(1), 271-293.
- Wallace, J. B., Webster, J. R. (1996). The role of macroinvertebrates in stream ecosystem function. Annual Review of Entomology, 41(1), 115-139.
- Warwick, R. M. (1993). Environmental impact studies on marine communities: pragmatical considerations. Australian Journal of Ecology, 18(1), 63-80.
30
11111
78301
20days
50days
10days
