Article Detail
Predicting Air Quality Index Based on Rainfall Patterns: A Machine Learning Approach with Mathematical Modelling
Keywords:
Air quality index
rainfall patterns
machine learning
predictive modeling
environmental monitoring
Abstract
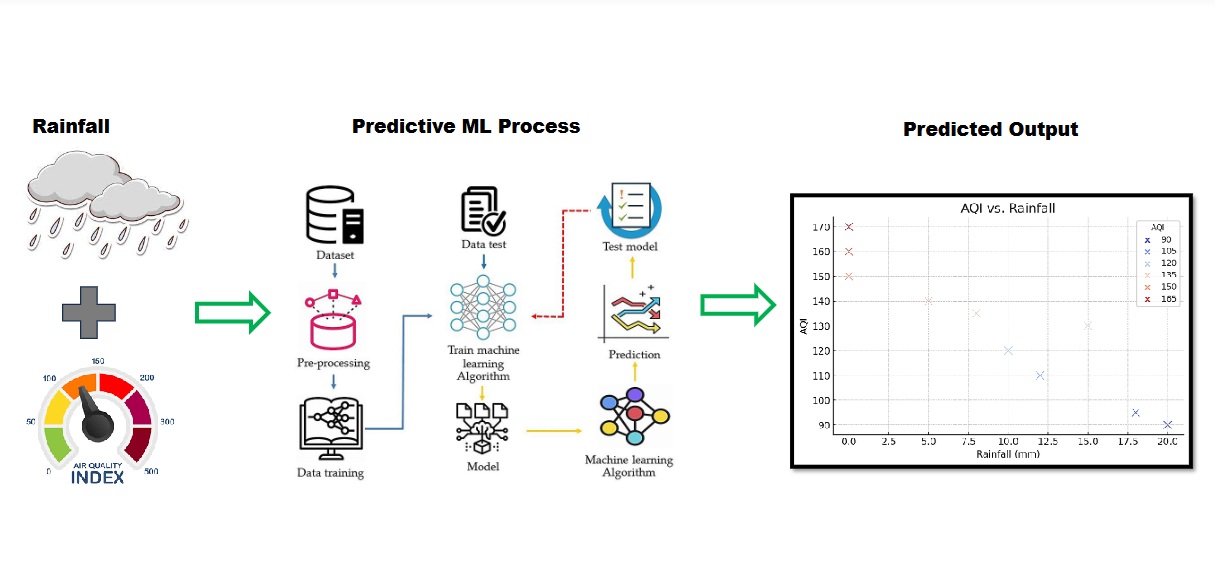
This study investigates the relationship between rainfall patterns and air quality index (AQI) in the Indian subcontinent using machine learning techniques. We developed a predictive model that incorporates rainfall data, including intensity, duration, and frequency, to forecast AQI values. Methodologically, rainfall and AQI data have been collected and preprocessed from various sources, including weather stations and air quality monitoring stations. These data were used to train and test the machine learning model, which was optimized using various techniques such as feature engineering and hyperparameter tuning. The model’s performance was evaluated using several metrics, including absolute mean error, root mean square error, and coefficient of determination. The proposed model demonstrated high accuracy in predicting AQI values, outperforming traditional statistical models. Our findings demonstrate that the predictive model can accurately forecast AQI values up to three days in advance, offering valuable insights for air quality management and policymaking, while also highlighting the significant influence of rainfall patterns, where heavy rainfall events improve air quality and dry periods lead to deterioration. The study underscores the critical role of machine learning-based models in environmental monitoring and prediction, suggesting that accurate AQI forecasts not only advance research in this field but also have vital implications for public health by helping mitigate the adverse effects of air pollution on human health.
References
- Abadi, M., Barham, P., Chen, J., Chen, Z., Davis, A., Dean, J., Devin, M., Ghemawat, S., Irving, G., Isard, M., Kudlur, M., Levenberg, J., Monga, R., Moore, S., Murray, D. G., Steiner, B., Tucker, P., Vasudevan, V., Warden, P., Wicke, M., Yu, Y., Zheng, X. (2016). TensorFlow: a system for large-scale machine learning. In: Proceedings Book. 12th USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation, 2-4 November 2016, Savannah, USA. pp. 265-283.
- Bergstra, J., Bengio, Y. (2012). Random search for hyper-parameter optimization. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 13, 281-305.
- Breiman, L. (2001). Random forests. Machine Learning, 45(1), 5-32.
- Chen, T., Guestrin, C. (2016). X G Boost: A scalable tree boosting system. In: Proceedings Book. 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, 13-17 August 2016, San Francisco, USA. pp. 785-794.
- Chen, X., Zhang, X., Guo, Y. (2018). Influence of meteorological parameters on urban air pollution: A study based on long-term observation. Atmospheric Environment, 193, 230-238.
- Fan, C., Li, J., Wang, S. (2020). Predicting air pollution with machine learning: A review of algorithms and applications. Environmental Pollution, 263, 114376.
- Field, A. (2013). Discovering statistics using IBM SPSS statistics. Sage Publications.
- Gao, M., Beig, G., Song, S. (2019). Ozone pollution prediction using meteorological and emission data with deep learning. Environmental Science & Technology, 53(18), 11038-11045.
- Gupta, P., Christopher, S. A. (2009). Particulate matter air quality assessment using integrated surface, satellite, and meteorological data. Environmental Science & Technology, 43(20), 7694-7700.
- Han, J., Kamber, M., Pei, J. (2011). Data mining: Concepts and techniques. Morgan Kaufmann.
- Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R., Friedman, J. (2009). The elements of statistical learning: Data mining, inference, and prediction. Springer.
- Hochreiter, S., Schmidhuber, J. (1997). Long short-term memory. Neural Computation, 9(8), 1735-1780.
- Huang, Y., Li, Y., Yang, Y. (2019). Understanding the effects of rainfall on air pollution: A study of urban regions. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 85, 42-50.
- Hyndman, R. J., Athanasopoulos, G. (2018). Forecasting: principles and practice. OTexts.
- James, G., Witten, D., Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R. (2013). An introduction to statistical learning with applications. Springer.
- Jiang, X., Li, R., Zhan, Y. (2019). Machine learning applications in air pollution prediction: A systematic review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 217, 894-906.
- Jiang, Z., Yang, S., Liu, Z., Xu, Y., Xiong, Y., Qi, S., Pang, Q., Xu, J., Liu, F., Xu, T. (2022). Coupling machine learning and weather forecast to predict farmland flood disaster: A case study in Yangtze River basin. Environmental Modelling & Software, 155, 105436.
- LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., Hinton, G. (2015). Deep learning. Nature, 521(7553), 436-444.
- Li, Y., Peng, T., Hua, L., Ji, C., Ma, H., Nazir, M. S., Zhang, C. (2022). Research and application of an evolutionary deep learning model based on improved grey wolf optimization algorithm and DBN-ELM for AQI prediction. Sustainable Cities and Society, 87, 104209.
- Little, R. J., Rubin, D. B. (2019). Statistical analysis with missing data. John Wiley & Sons.
- MathWorks. (2021). MATLAB documentation. The MathWorks.
- McKinney, W. (2010). Data structures for statistical computing in Python. In: Proceedings Book. 9th Python in Science Conference, 28 June - 3 July 2010, Texas, USA. pp. 56-61.
- Pedregosa, F., Varoquaux, G., Gramfort, A., Michel, V., Thirion, B., Grisel, O., Blondel, M., Prettenhofer, P., Weiss, R., Dubourg, V., Vanderplas, J., Passos, A., Cournapeau, D., Brucher, M., Perrot, M., Duchesnay, E. (2011). Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 12, 2825-2830.
- Tang, L., Zhou, J., Zhao, M. (2021). Rainfall and air pollution: A multi-city case study. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 12(4), 456-469.
- Wang, J., Sun, Y. (2021). Hybrid deep learning approaches for air quality prediction. Environmental Research, 195, 110849.
- Wang, L., Wu, S., Yu, C. (2022). The role of meteorological factors in air pollution forecasting: A machine learning perspective. Atmospheric Environment, 262, 118629.
- WHO. (2021). WHO global air quality guidelines: Particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), ozone, nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide and carbon monoxide. World Health Organization. Available at: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240034228 (04.05.25).
- Willmott, C. J., Robeson, S. M., Matsuura, K. (2012). A refined index of model performance. International Journal of Climatology, 32, 2088-2094.
- Xu, H., Zeng, W., Guo, B., Hopke, P. K., Qiao, X., Choi, H., Luo, B., Zhang, W., Zhao, X. (2020). Improved risk communications with a Bayesian multipollutant air quality health index. Science of the Total Environment, 722, 137892.
- Yang, W., Deng, M., Xu, F., Wang, H. (2018). Prediction of hourly PM2. 5 using a space-time support vector regression model. Atmospheric Environment, 181, 12-19.
- Zhang, K., de Leeuw, G., Yang, Z., Chen, X., Jiao, J. (2020). The impacts of the COVID-19 lockdown on air quality in the Guanzhong Basin, China. Remote Sensing, 12(18), 3042.
- Zhang, Y., Ma, Y., Feng, F., Cheng, B., Shen, J., Wang, H., Jiao, H., Li, M. (2021). Respiratory mortality associated with ozone in China: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Environmental Pollution, 280, 116957.
- Zhao, H., Chen, K., Liu, Z., Zhang, Y., Shao, T., Zhang, H. (2021). Coordinated control of PM2. 5 and O3 is urgently needed in China after implementation of the “Air pollution prevention and control action plan”. Chemosphere, 270, 129441.
- Zhao, P., Zhang, X., Chen, H. (2022). Meteorology-driven air quality forecasting using hybrid models. Science of the Total Environment, 814, 152561.
- Zheng, J., Su, M., Ying, W., Tong, J., Pan, Z. (2021). Improved uniform phase empirical mode decomposition and its application in machinery fault diagnosis. Measurement, 179, 109425.
30
11115
78305
20days
50days
10days
